-
Homogenous Reactions:
The reaction which is carried out in only one phase is called a homogenous reaction.
-
Heterogenous Reactions:
The reaction which is carried out in more than one phase is known as heterogenous reaction.
-
Reaction Rate :
The reaction rate can be defined on the basis of:
- Volume of reacting fluid:

2. Unit of mass fluid :

3. Volume of reactor :
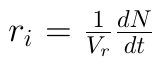
4. Surface of solid :
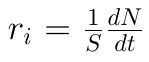
5. Volume of solid:

Reaction rate is dependent upon the rate of system i.e. :
- temperature,
- pressure and
- composition.
Types of Reactions:
- Single Reaction : When a single stoichiometric reaction and single rate equation is selected to represent the progress of reaction, it is called a single reaction.
- Multiple Reaction : When more than one stoichiometric equation are used to represent the progress of reaction, it is called a multiple reaction.
Types of multiple reactions:
i. Series Reaction :
![]()
ii. Parallel Reaction :
(a) Competitive reaction

(b) Side by side reaction

(c) Parallel but in series

Elementary Reaction:
The reaction in which rate depends upon stoichiometry of the reaction is called an elementary reaction.
e.g.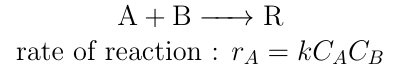
Non-elementary reaction :
The reaction in which rate does not depend upon stoichiometry of the reaction is called an non-elementary reaction.
e.g.
![]()
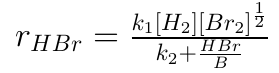
Forward Reaction:
If the reactant in the reaction is formed or produced the reaction is called a forward reaction.
Reverse Reaction:
If the reactant in the reaction is disappearing the reaction is called a reverse reaction.
e.g. ![]()
Here: ![]() is rate of forward reaction and –
is rate of forward reaction and –![]() is the rate of reverse reaction written respectively as :
is the rate of reverse reaction written respectively as :

It is important to remember that : ![]()
Chain Reaction:
1. Reaction Initiation :
![]()
2. Reaction Propogation :
![]()
3. Reaction Termination :
![]()
***************************
Discover more from Dr. Ganesh Visavale
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.